Credible, interactive virtual hardware experiences
The only hardware-inspired, scalable way to bring credible, high-fidelity interactive lab experiences to students off-campus.
QLabs Controls
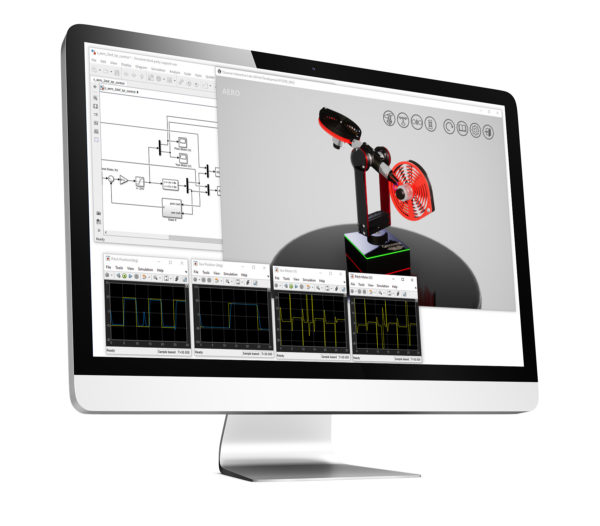
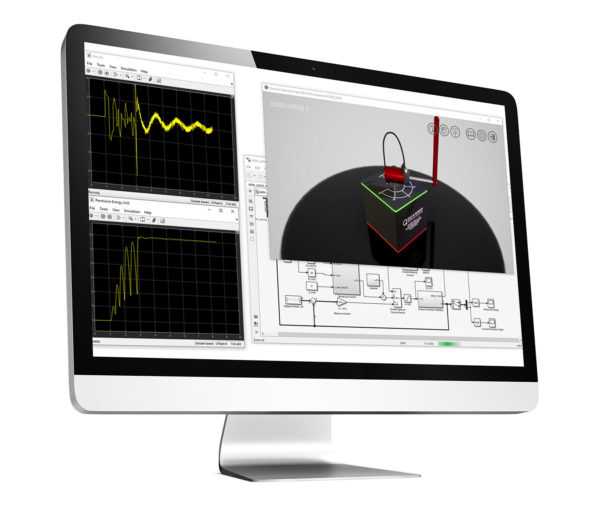
QLabs Controls is a collection of virtual laboratory activities that supplement traditional or online control systems courses. The virtual hardware labs are based on Quanser QUBE-Servo 2 and Quanser AERO systems which allows you to combine physical and virtual plants to enrich lectures and in-lab activities and increases engagement and students’ learning outcomes in class-based or online courses.
QLabs Robotics
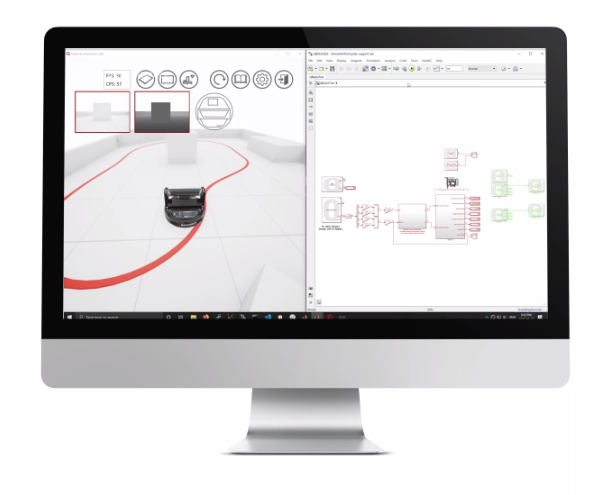
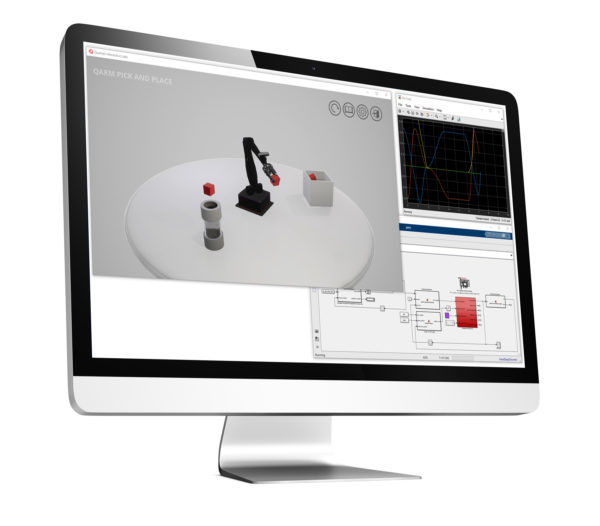
QLabs Robotics is a collection of virtual laboratory activities that supplement traditional or online robotics courses. The virtual hardware labs are based on Quanser QArm robotic manipulator and QBot 2e mobile ground robot. The virtual twins of these robots are fully instrumented and dynamically accurate, allowing users to measure simulated sensors, including video and depth data, interact with virtual environments, and work with the same code created for the “real” robots. With QLabs Robotics, you can combine physical and virtual plants to enrich your lectures and in-lab activities and increases engagement and students’ learning outcomes in class-based or online courses.
QLabs Virtual QArm
Same as the physical QArm, the virtual system is a 4 DOF serial robotic manipulator with a tendon-based two-stage gripper and an RGBD camera.
QLabs Virtual QBot 2e
Same as the physical QBot 2e, the virtual system is an autonomous ground robot featuring built-in sensors and vision system.
QLabs Virtual Quanser AERO
Same as the physical Quanser AERO, the virtual system is a dual-rotor helicopter model that can be reconfigured for 1 DOF attitude, 2 DOF helicopter, or half-quadrotor experiments. Rotary encoders measure the angular position of the propeller DC motors, the speed of the motors is measured through a software-based tachometer.
QLabs Virtual QUBE-Servo 2
Same as the physical QUBE-Servo 2, the virtual system features a DC motor with the inertia disk and inverted pendulum modules. Rotary encoders measure the angular position of the DC motor and pendulum. The motor angular velocity is measured through a software-based tachometer.
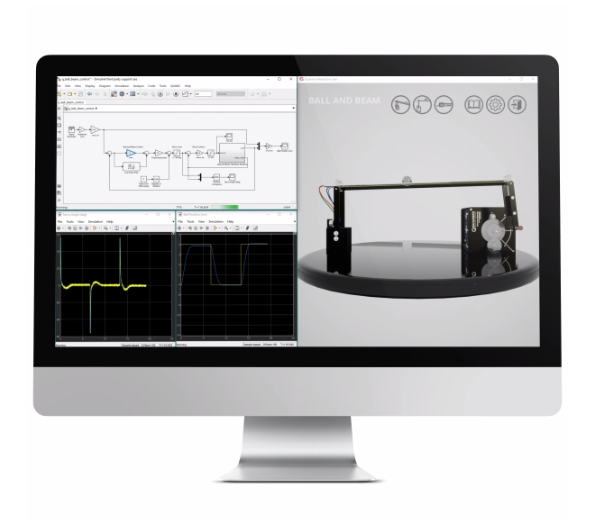
QLabs Virtual Ball and Beam
Same as the physical Ball and Beam, the virtual system features a track on which a ball is free to roll. The track is effectively a potentiometer, outputting a voltage proportional to the position of the ball. The tilt angle of the track is controlled by the Rotary Servo’s DC motor.
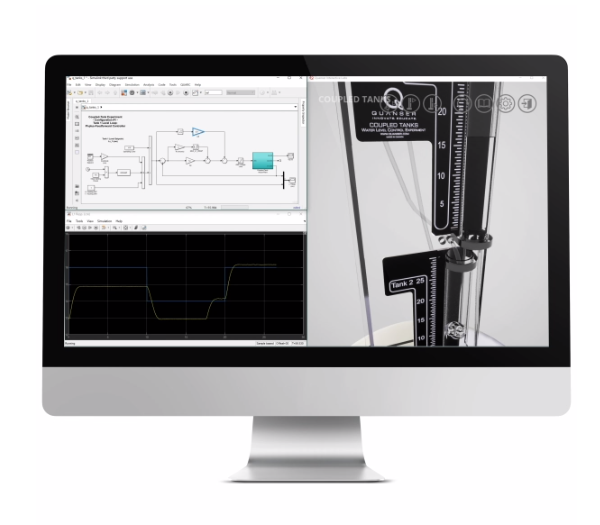
QLabs Virtual Coupled Tanks
Same as the physical Coupled Tanks, the virtual system features a single pump and two tanks. Each tank is instrumented with a pressure sensor to measure the liquid level. The different outflow valves configurations allow to direct the flow of the liquid, while the flow rate can be changed by using outflow orifices of different diameters.
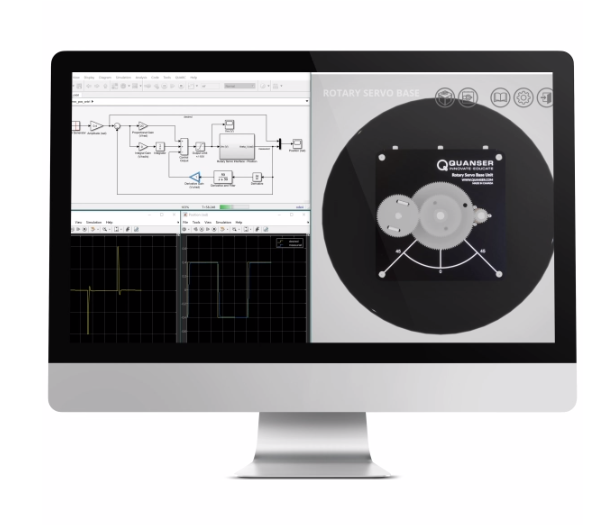
QLabs Virtual Rotary Servo
Same as the physical Rotary Servo Base Unit, the virtual system features a DC motor that drives a smaller pinion gear. This gear is fixed to a larger middle gear that rotates on the load shaft. The position of the load shaft is measured using a high-resolution optical encoder or a potentiometer.